
 [罗戈导读]无人货架真的是伪命题,小商店到处都是模式太重,营收太少。零售要解决的根本不是前端的问题,零售要解决的真正是供应链和货品质量的问题,无人货架在未来的某个时间会以另外一种方式回归。
[罗戈导读]无人货架真的是伪命题,小商店到处都是模式太重,营收太少。零售要解决的根本不是前端的问题,零售要解决的真正是供应链和货品质量的问题,无人货架在未来的某个时间会以另外一种方式回归。

无人货架真的是伪命题,小商店到处都是模式太重,营收太少。零售要解决的根本不是前端的问题,零售要解决的真正是供应链和货品质量的问题,无人货架在未来的某个时间会以另外一种方式回归。即使现在,也在硬件上不断迭代降低成本。因为购物越来越“服务化”,无人就符合服务体验。
蛤蟆集团认为无人货架这个模式无任何机会可言。工作场景的这种需求会由企业园区便利店完成,企业园区便利店会演变成线上+线下的新零售模式,导购可以提升一家零售店的60%以上的销售,无人售卖机 将会替代无人货架,苏宁小店我一直特别看好。
蛤蟆集团觉得包括无人货架、无人售卖机器之类的东西都没戏。很简单,只要从市场规模/真伪需求/盈利模式/护城河四个角度分析即可。名创优品和优衣库、无印良品,他们有啥服务,开街铺好的很。后端是每个成功企业都一定要非常优秀的,但是需不需要工厂则未必。只要供应链管理的好,不需要工厂。
人工越来越贵,随着无人货架的成本从2万降低到3000,供应链管理的效率提升,很多场景就会改变。无人货架上架的都是保质期长的垃圾食品,而这种垃圾食品的味道真的不好。无人货架频繁的送货到货架,运营成本太高仓储成本高,要在一个城市随时补货,需要很高的仓储成本,办公室的消费环境有问题,大公司有自己零食区,很多公司上班不能吃零食,公司楼下各种便利店,货架太小,可挑选目标太少1、喜欢吃零食的都会觉得零食味道好。2、无人货架不用频繁送货,一天补1-2次即可。3、仓储如果是个问题,可口可乐不用活了,可口可乐要给每个便利店补货的。4、建议去看看其他公司,95%以上的办公室没有零食区。
从需求端来看,传统的零售三角模型,是满足消费者多选/便利/廉价的需求,无人货架之类的模式,很显然是为了满足其中单一要素即“便利”,仅此而已。那么就要判断,这个便利是不是公司场景的真实需求,或者说,消费者会不会因为便利这个单一要素,愿意接受“略高的价格”(一般都会比便利店贵些)、“较远的生产日期”(这个是最尴尬的)、“差异化定位的产品”(为提升毛利选择的非普通大众常见品)…
从经营角度来看,无人货架系列产品盈利模型非常不清晰,包括货品丢失/临期产品处理/上架下架管理等一系列涉及供应链整个环节诸多问题无法解决;
毫无护城河可言。这就更不用说了。
好了不墨迹这个问题了,直接本我们的Kanban材料!
topics主题
Section 1: What is Kanban?什么是看板?
Section 2: Two-card Kanban Systems 2张看板卡系统
Section 3: Kanban Calculation 看板的计算
我们这一期讲这些:
Section 4: Managing the Kanban System 管理看板系统
Section 5: Kanban System Implementation 看板系统的实施
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Section 4: Managing the Kanban System 管理看板系统
The 6 prerequisites 6个必要条件
The 6 golden rules 6条金科玉律
Kanban circulation steps 看板循环步骤
Integration with the planning system与计划系统进行整合
What Does it Mean to Manage the Kanban System?这对管理看板系统的意义?
Implement the 6 Prerequisites first 首先实施6个必要条件
Build a foundation of stability demand创造一个需求平稳的基础
Build process capability and responsiveness创造制程能力及应答
Follow the 6 Golden Rules 按照6条金科玉律
Train and practice until it becomes second nature培训及练习直到成为第2个本性
Material conveyance system supports the pull system物料匀速系统支持拉动系统
Integrate with the planning system与计划系统进行整合
Responsibility for add / removal of cards based on demand and capability changes负责根据需求及产能的变更来增加或减少看板卡
The kanban cards replace other paper instructions the system must fail if kanban cards go missing看板卡替代其他的纸质指示当看板卡丢失时系统一定会失效。
The 6 Prerequisites of Kanban Systems看板系统的6个必要条件Stable and predictable demand平稳及可预测的需求
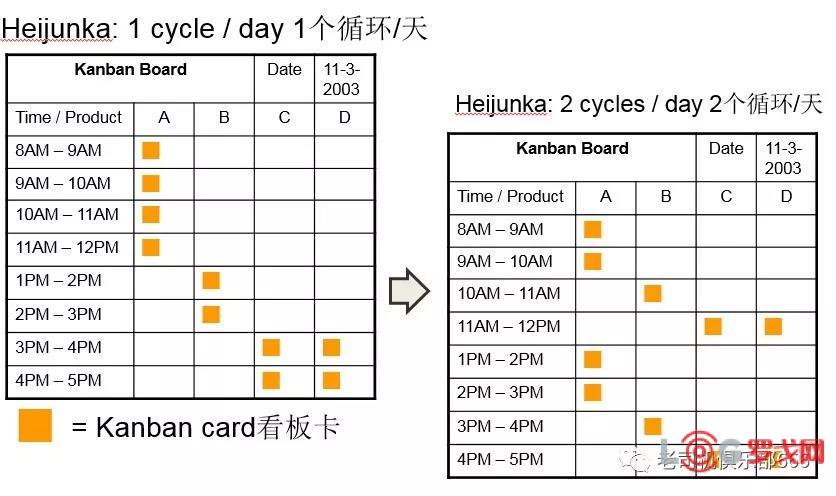
Levelled Production (Heijunka) (平化)
生する物(れにびついた物)のと量を平均化することをいう。ジャストインタイムに生するための前提条件である。
确保生产活动期间零件种类、量、都到均等,JIT式生产的前提。
Small lot sizes through quick changeover通过快速换模时间小的生产批量
Information linked to material信息与物料链接
Defect-free delivery无缺陷的交付
Attach kanban container看板附在周转箱上
Continuous improvement discipline持续改进记律
5S discipline 5s纪律
Use kanban to expose and problems 使用看板来暴露问题
Kanban Prerequisite #1: Heijunka看板必要条件 #1
Heijunka = Averaging of both production volume and mix 生产种类及生产量平均化
WITHOUT heijunka, the kanban system will have:没有均衡化, 看板系统将会:
Excess resources to respond to demand swings,需要多余的资源来应对需求的振幅
Excess inventory levels (setting kanban card quantity at maximum demand), or需要多余的库存(根据最大的需求来设置看板卡数量)
The need to constantly adjust kanban quantities and materials in process up and down to match demand不断的需要调整看板数量及WIP数量来满足需求
Kanban Prerequisite #1: Heijunka看板必要条件#2: 均衡化生产
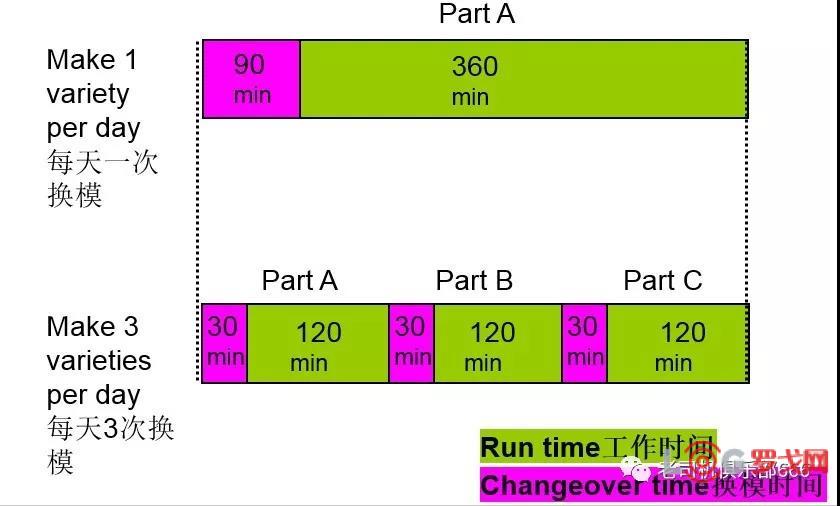
Prerequisite #2: Small Lot Production必要条件#2:小批量生产
Minimize set-up times and other factors that increase lot size
最小化开机时间及其他因素来提高批量大小
WITHOUT small lot sizes, the kanban system will have:
没有小批量生产,看板系统将:
More kanban cards due to long replenishment lead times caused by large batch sizes,因为大的批量造成的补料时间长则需要多的看板
Off-line storage areas for parts not needed in the kanban system (overproduction), and线外的存储区域不在看板系统内(过量生产)
Less responsiveness to downstream changes in customer pull, resulting in more inventory and related waste. 在客户拉动下游的变化反应少,造成更多的库存及相应的浪费
Prerequisite #3: Defect-Free Delivery必要条件 #3: 无缺陷的交付
The container quantity must be correct and defect-free
周转箱中的数量必须正确且无缺陷
WITHOUT defect-free delivery, the kanban system will have:
如果不能无缺陷的交付,看板系统将会:
A mismatch between the information and the actual materials 实际物料不能满足信息要求
Shortages when there are defects, or当出现不良时导致缺料
“Just in case” inventory within processes to cover for defects, defeating the purpose of the kanban system.工序的库存满足不良,看板系统默认的目的
“Three Don’ts” of Built-in Quality 3个不
Don’t accept poor quality 不接受不良品
Don’t make poor quality 不制造不良品
Don’t ship poor quality 不出货不良品
This is easy to say, but impossible to do without a supporting system of built in quality.说来容易,但是如有没有一个支持的质量体系是做不到的
Prerequisite #3: Defect-Free Delivery必要条件#3 无缺陷的角度
In-process inspection to guarantee quality过程检验来保证质量
“Stop and fix” mentality“停下来解决问题”
Root cause countermeasures根本问题对策
Prerequisite #4: Attach Kanban to Containers必要条件#4 看板附在周转箱
Information and materials always travel together信息及实物通常一起移动
WITHOUT kanban attached to containers, the kanban system will have:如果看板没有附在周装箱上,则看板系统将会
Mismatches between the information and the actual materials, and信息及实际的物料无法对应
Loss of the visual control function of kanban to instruct production or movement of goods.失去了目视化管理的工程来指示产品生产及移动
Prerequisite #5: 6S Discipline必要条件#5 5S 的纪律
Material location, quantity and orientation must be controlled物料的地址,数量,方向必须被控制
WITHOUT 5S discipline, the kanban system will have:没有做好5S,看板系统将会:
Shortages due to misplaced materials,物料摆放错误造成的缺料。
Delays due to searching for misplaced materials, and因为找料而出现的延误
Excess materials due to lack of adherence to controls.因没有严格遵守控制而 造成的多余物料
Use Kanban to Expose and Solve Problems必要条件#6 使用看板来曝光及解决问题
Use kanban as a tool for process improvement NOT to hide problems with inventory!使用看板来实现过程改进-不隐藏库存的问题
WITHOUT exposing and solving problems, the kanban system will have:在不能曝光及结果问题的情况下,看板系统将会:
Often more inventory in the beginning than without kanban,库存在最开始的时候经常高于未使用看板的时期
Chronic problems that make people want to increase buffers, and慢性的问题造成人们愿意去增加缓冲的库存
A disconnection with the continuous improvement culture.与持续改进的文化脱节。
How to Run the Kanban System 如何来运行看板系统
1、The downstream process withdraws items they need下游工序补充所需要的物料
2、The upstream process makes what is withdrawn上游工序制造所补充的物料
3、The kanban always stays with the material看板要与物料放在一起
4、Wrong or bad materials are never allowed downstream错误及坏品不允许流到下游工序
5、Kanban is used only for minor (±10%) adjustments看板仅用于小的调整 (±10%)
6、Kanban quantities are continuously reduced看板数量将持续减少
Kanban Circulation Steps看板循环的步骤
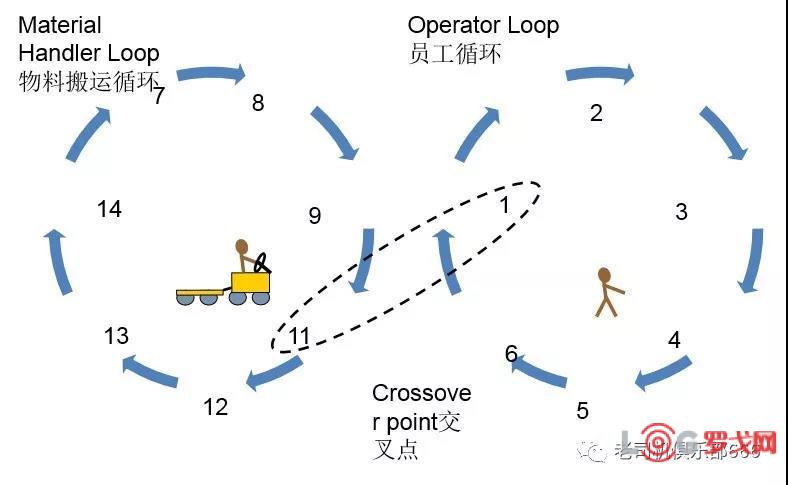
The operator:员工:
1、Receives instruction to produce in the form of production instruction kanban (from step 11)收到生产指示看板来指示生产
2、Takes first piece from raw material (parts) storage area at beginning of line
3、Removes withdrawal kanban card when the first part is taken from container当第一个物料从周转箱取出时取下补料看板卡
4、Places the withdrawal kanban card in the kanban post将补料看板卡放在看板分发处
5、Place the production instruction kanban in the container of raw material放置生产指示看板到原材料的周转箱中
6、Puts the completed parts with their production instruction cards in the finished goods supermarket将生产完毕的零件与生产指示卡放入成品的超市中
7、When to Pull a Kanban Card?什么时候去拉动一张看板卡
8、Pull the kanban card when the first piece is taken from the container当第一个物料从周转箱周取出时拉动看板卡
9、Keeps the rule simple and consistent保持规则的简单及一致性
10、Use the delivery cycle on the kanban itself to specify when the next full container will arrive – not too early当下一个满箱物料将要到达时使用看板自身的交付循环来明确说明。
Receives instruction to produce (from step 10)…收到指示进行生产(从工序10)
Key points关键点
Produce only the quantity specified on the production instruction cards仅生产看板指示卡上标识的数量
Produce in the sequence that the production instruction cards were removed根据生产指示卡的顺序进行生产
The material handler:物料员
Collects withdrawal cards from kanban post after a fixed period of time (if far away) or after a fixed quantity of cards (if nearby)在一个固定的时期从看板架上收集补料卡或者在一个固定的看板数量后
Transports the withdrawal cards to the upstream process supermarket将这些补料看板卡运送至上游工序的超市
Withdraws the parts and quantities specified on the kanban cards根据看板卡补充相应的零件及数量
Removes the production instruction cards from the parts containers that were withdrawn当补料时将生产指示看板从物料箱中取出
Places the kanban cards in the production instruction kanban post将看板卡放置到生产指示看板架上
Attach the withdrawal kanban cards to the containers withdrawn将取料看板卡附在物料周转箱上
Transports the parts in their containers with withdrawal kanban cards attached to the downstream process 将附有补料看板卡的物料运送至下游工序
Places parts containers with withdrawal kanbans attached in designated incoming goods store将附有补料看板卡的物料箱放置在设计好的来料存储区域
Key points关键点
Conveyance within the factory is commonly based on a fixed quantity, (variable timing)在工厂内运输通常基于一个固定的数量(时间可变)
Conveyance between supplier companies and the factory is typically based on a fixed time (variable quantities)在供应商及工厂间运输通常基于一个固定的时间(数量可变)
Kanban Circulation SOP看板循环标准作业
Create standard operating procedure (SOP) documents for team member training创建一个标准的作业指导来培训员工
Use visuals使用目视化
Conduct training hands-on手把手
Kanban System Roles and Responsibilities看板系统的规则及职责
Kanban System Implementation看板系统的实施
Kanban system deployment phases看板系统实施阶段
Kanban system design tips看板系统设计的提示
Kanban implementation pitfalls看板实施的陷阱
Section 5: Kanban System Implementation 看板系统的实施
Kanban System Implementation看板系统的实施
Kanban system deployment phases看板系统实施阶段
Kanban system design tips看板系统设计的提示
Kanban implementation pitfalls看板实施的陷阱
Kanban System Deployment Phases看板系统实施阶段
Kanban Systems Design Tips看板系统设计提示
Packaging包装
Containers reusable 包装箱可循环使用
Pallets purpose-built only 卡板-仅定制
Lot sizes批量大小
Quantity based on pieces (not days’ supply)数量基于单个(而不是一天的供应)
Increase or decrease based on demand根据需求进行增加或减少
Order point订单点
Placing the signal kanban and material preparation kanban下信号看板及物料准备看板
Quantity-based withdrawal, but timing-based position基于数量的补料,但是基于时间的位置
Container design周装箱设计
Safety first安全第一
Container quantity for signal kanban should be less than one day’s usage信号看板的包装数量必须小于1天的用量
Also consider factors such as material presentation to the customer, weight, and space taken at the line也要考虑其他因素例如物料的陈列,重量及生产线需要的空间
Kanban Implementation Pitfalls看板实施的陷阱
Using kanban to manage inventories that should not be there in the first place使用看板来管理库存不能放在第一位
Connect processes and eliminate through one-piece flow通过单件流来连接工序来消除看板
Setting safety stock and buffers set too high安全库存及缓冲库存设置的太高
2.Having more inventories than when using MRP push比使用MRP相比库存更高
Attempting kanban for seasonal items在季节性产品上尝试看板
Not changing MRP lead-time offsets, such as when batch sizes have been reduced当批量大小减小时没有变更MRP前置时间的设置
Using kanban to cover up problems such as machine reliability, scrap or changeovers使用看板来弥补问题例如机器可靠性,报废或者换模
3.Using both kanban and MRP systems to release material使用看板及MRP来释放物料
Group Exercises团队练习
Suggested actions建议的行动
Review value stream maps for areas where kanban are needed查看价值流程图来发现需要看板的地方
Calculate kanban quantities 计算看板数量
Review current state of site against kanban prerequisites查看现状及看板必要条件进行对比